
Frequent Takeaway Food Consumption is Linked to Cardiometabolic Risk!!
- January 9, 2026
- MIND's Lab Publishing
 Consequent to improved economic conditions and the rise in the use of internet-based food delivery applications (Apps), the young and the middle-aged adults are frequently resorting to consumption of takeaway foods. While this may be convenient for the busy, working people, such foods are often nutritionally poor, being energy-dense and low in vegetables and fruits.
Consequent to improved economic conditions and the rise in the use of internet-based food delivery applications (Apps), the young and the middle-aged adults are frequently resorting to consumption of takeaway foods. While this may be convenient for the busy, working people, such foods are often nutritionally poor, being energy-dense and low in vegetables and fruits.
Frequent consumption of such takeaway foods is associated with systemic inflammation and increased cardiometabolic risk (insulin resistance, adverse effects on glucose metabolism, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia).
A study conducted by Wen H et al., recently published in Food Science & Nutrition, examined the association between frequent consumption of takeaway foods and inflammatory markers and cardiometabolic risk. Frequent consumption of takeaway foods (≥6 times/week) was found to be a pro-inflammatory diet and was associated with unfavorable cardiometabolic profile (higher energy, increased inflammatory markers, lower HDL [good] cholesterol, higher triglycerides, higher fasting glucose, serum insulin, and insulin resistance (see the Graphic for the study snapshot).
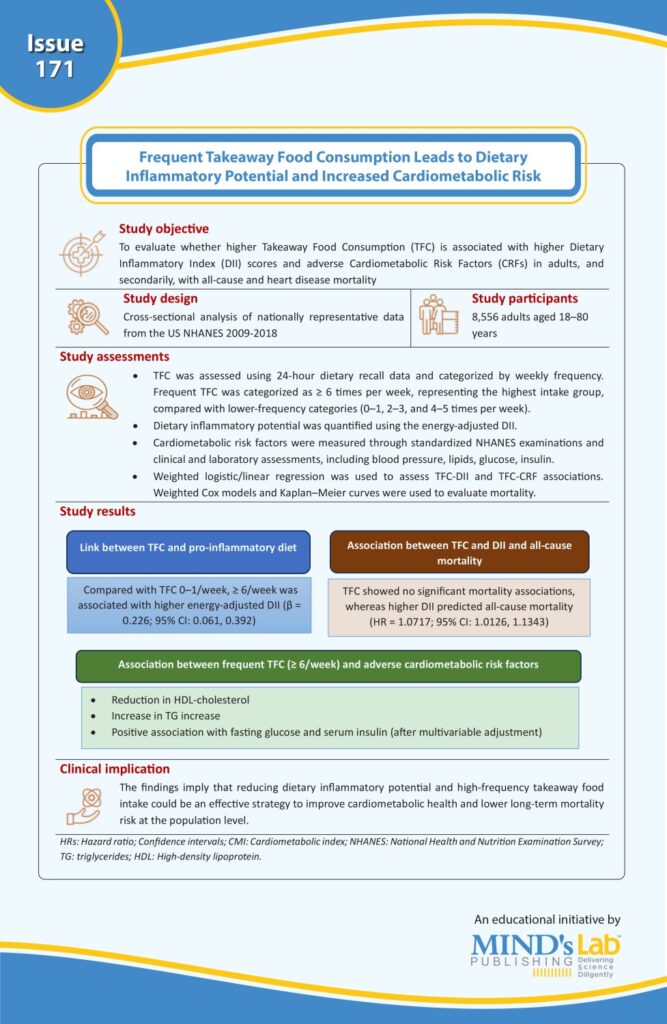
(Source: Wen H, Li S, Hun M, Yang Y, Xiong L, Wen H, Mao L, Yu D, Chen M, Wang Z, Zhao TC, Zhao M, He Q. Takeaway food consumption, dietary inflammatory index, and cardiometabolic risk factors in US adults: Findings from NHANES (2009-2018). Food Sci Nutr. 2025;13(12):e71316. Doi: 10.1002/fsn3.71316)
